PCB Materials: A Comprehensive Comparison of FR4, FR5, and Other Options
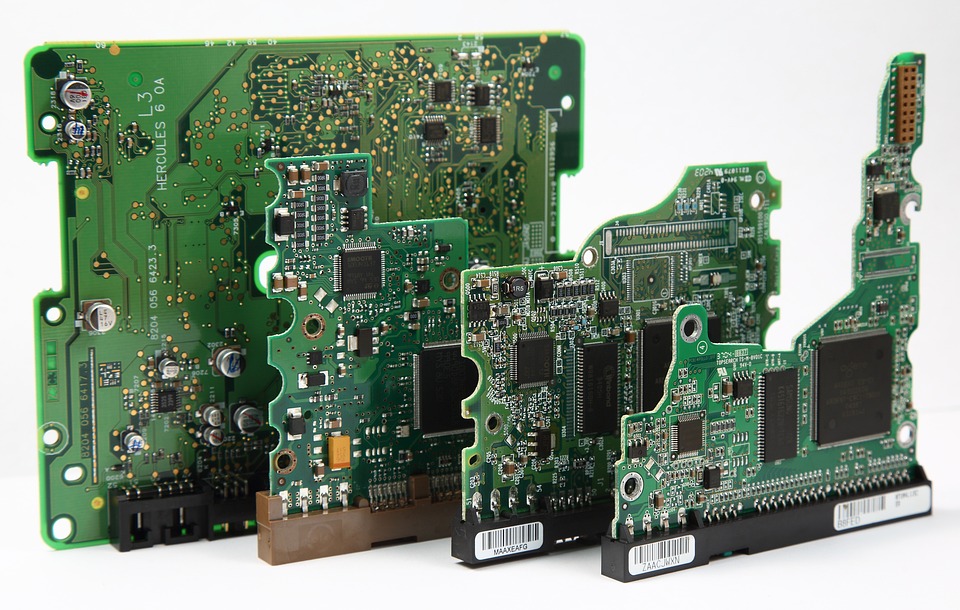
In the design of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), the selection of the appropriate material is crucial to ensure that the board can efficiently transmit data signals, manage high-frequency operations, and meet performance requirements while ensuring reliability, thermal stability, and cost-effectiveness. One of the primary tasks in the selection of the suitable PCB material involves choosing among a variety of commercially available epoxy glass-based printed circuit board (FR4/5) substrates, flexographic circuits (Rogers/Micro-Solder), flex-Rigid materials, and metal substrates, in addition to exotic materials with specialty properties like bismaleimide-triethylene (BTT-E).
FR4 (FRP)
FR4, commonly known as Frangible Resistant Fireproof Material-4 (or FR4 epoxy glass laminated material for simplified terms) represents the original generation of copper-reinforced substrate materials (referred to as FR series: FR3 FR4 and so on).
#### Advantages
- Panasonic/EICOS) a leading technology producer of ECE materials)
offers FR4 based on BSG ( Bromo Styrenne Glyxine) chemical.
FR4 has exceptional tensile and warp resistance along with excellent flexibility while being simple in design.
FR4 includes resin-based fiberglass epoxy material) It has also found applications.
Additionally, a resin-based.
composite of phenol resin. is a phenol resin for thermosets used in many construction projects.)
• FR4 board thickness levels span from.050 inches 7.65 to 100 in.5 of the actual total.
thickness; it contains at least an internal layer structure.)
1; the other component.
The primary concern or disadvantage about PCBs
Consider:cost limitations‘are mainly the material expense and board structure complexity).