PCB Assembly for Medical Devices: Ensuring Compliance and Reliability
PCB Assembly for Medical Devices: Ensuring Compliance and Reliability
When it comes to medical devices, the quality and reliability of the printed circuit board (PCB) assembly are crucial for ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the device. Medical devices, such as implantable devices, diagnostic equipment, and therapeutic equipment, rely on PCBs to perform complex functions and interact with patients. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the PCB assembly meets the highest standards of quality, reliability, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Compliance with Regulatory Requirements
The medical device industry is heavily regulated, and manufacturers must comply with various regulations and standards to ensure the safety and effectiveness of their devices. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates medical devices, and manufacturers must comply with the FDA’s Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) guidelines and the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) framework.
In Europe, the Medical Device Regulation (MDR) framework is used to regulate medical devices, and manufacturers must comply with the European Union’s (EU) GMP guidelines. Additionally, other international regulations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 13485 standard, also apply to medical device manufacturers.
To ensure compliance with these regulations, PCB assembly manufacturers must implement quality management systems that meet the requirements of the relevant regulations. This includes the implementation of a quality management system that covers design, manufacturing, testing, and distribution of the PCB assembly.
Reliability and Performance
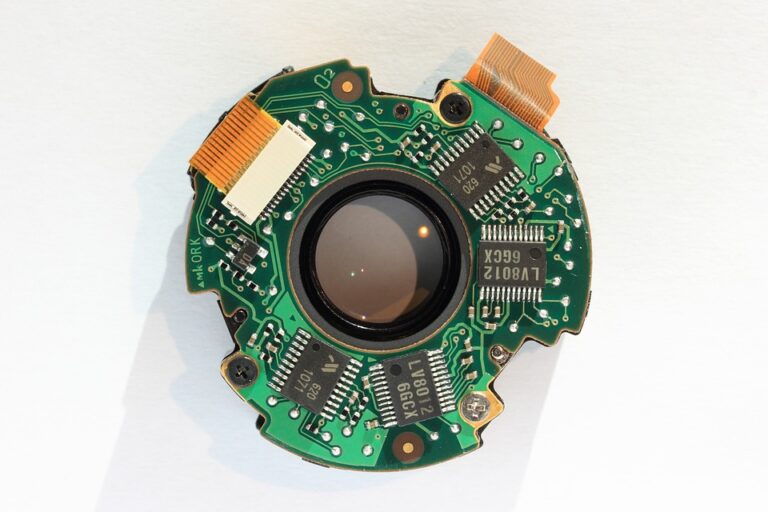
Reliability and performance are critical aspects of PCB assembly for medical devices. Medical devices are often used in critical applications where failure can have serious consequences. Therefore, PCB assemblies must be designed and manufactured to meet the highest standards of reliability and performance.
To ensure reliability and performance, PCB assembly manufacturers must implement a range of quality control measures, including:
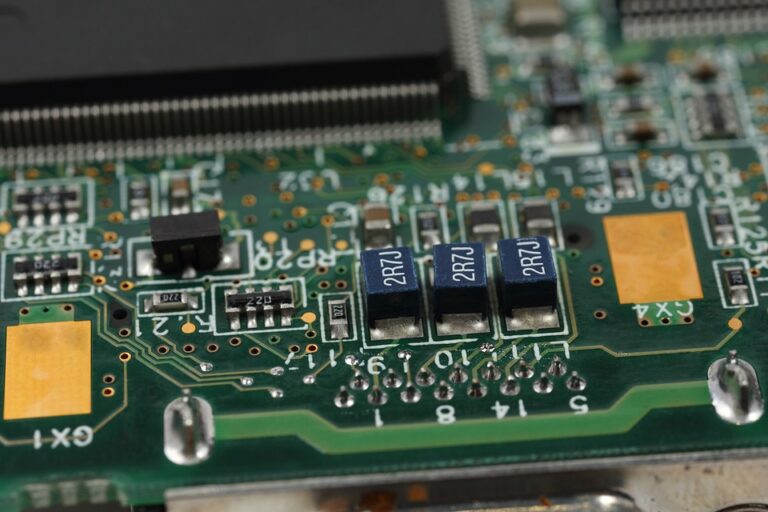
- Surface mount technology (SMT) assembly with high-quality components
- Inspection and testing of PCB assemblies for defects and errors
- Reliability testing, such as temperature cycling, vibration, and humidity testing
- Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) testing to ensure compliance with relevant standards
Design and Manufacturing
Design and manufacturing are critical aspects of PCB assembly for medical devices. The design of the PCB assembly must take into account the specific requirements of the medical device, including its intended use, performance requirements, and regulatory requirements.
PCB assembly manufacturers must use a range of design and manufacturing techniques to ensure that the PCB assembly meets the required specifications. These techniques include:
- Computer-aided design (CAD) software to design the PCB assembly
- SMT assembly with high-quality components
- Thermal management techniques to ensure optimal operating temperatures
- Testing and inspection of PCB assemblies to detect defects and errors
Testing and Inspection
Testing and inspection are critical aspects of PCB assembly for medical devices. PCB assemblies must be tested and inspected to ensure that they meet the required specifications and are free from defects and errors.
PCB assembly manufacturers must use a range of testing and inspection techniques to ensure the quality and reliability of the PCB assembly. These techniques include:
- Visual inspection of PCB assemblies for defects and errors
- Functional testing of PCB assemblies to ensure that they meet the required specifications
- Reliability testing, such as temperature cycling, vibration, and humidity testing
- EMC testing to ensure compliance with relevant standards
Conclusion
PCB assembly for medical devices is a critical aspect of the medical device manufacturing process. To ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and reliability and performance, PCB assembly manufacturers must implement quality management systems, design and manufacture PCB assemblies with the highest standards of quality and reliability, and test and inspect PCB assemblies to detect defects and errors.
In conclusion, PCB assembly for medical devices requires a high level of expertise, experience, and quality control. PCB assembly manufacturers must be able to design and manufacture PCB assemblies that meet the specific requirements of the medical device, and ensure that the PCB assembly is reliable and performs as expected.
FAQs
Q: What are the main challenges in PCB assembly for medical devices?
A: The main challenges in PCB assembly for medical devices include ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, designing and manufacturing PCB assemblies that meet the specific requirements of the medical device, and ensuring the reliability and performance of the PCB assembly.
Q: What are the most common defects and errors in PCB assembly for medical devices?
A: The most common defects and errors in PCB assembly for medical devices include solder joint defects, component placement errors, and electrical testing failures.
Q: How can PCB assembly manufacturers ensure compliance with regulatory requirements?
A: PCB assembly manufacturers can ensure compliance with regulatory requirements by implementing quality management systems that meet the requirements of the relevant regulations, and by ensuring that the PCB assembly meets the required specifications and is free from defects and errors.
Q: What are the benefits of using surface mount technology (SMT) assembly in PCB assembly for medical devices?
A: The benefits of using SMT assembly in PCB assembly for medical devices include increased density, reduced weight, and improved reliability and performance.
Q: What are the most common testing and inspection techniques used in PCB assembly for medical devices?
A: The most common testing and inspection techniques used in PCB assembly for medical devices include visual inspection, functional testing, reliability testing, and EMC testing.